How to make your balance dance?
Have you ever been to the Superfluid Dashboard and seen the balance of a user dancing like in the GIF below? This is because the balance of Super Tokens is constantly being updating, with each block.
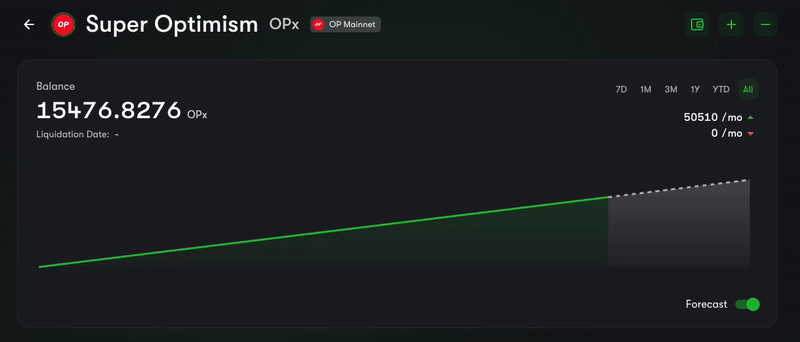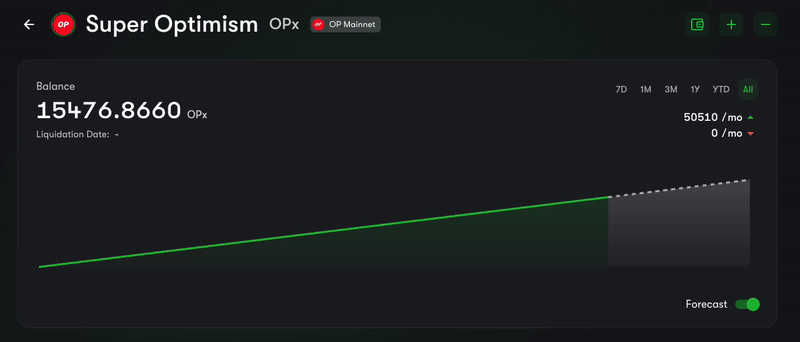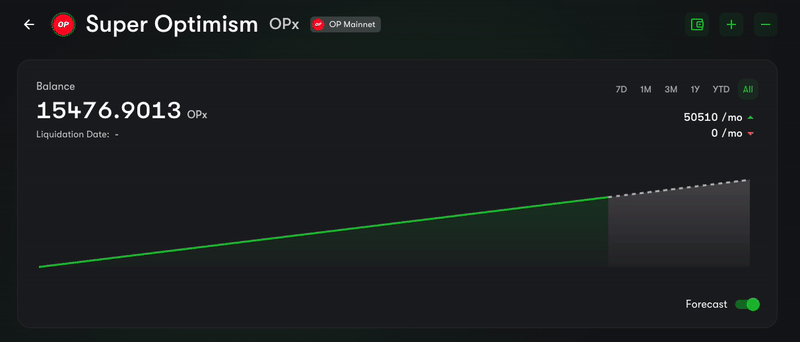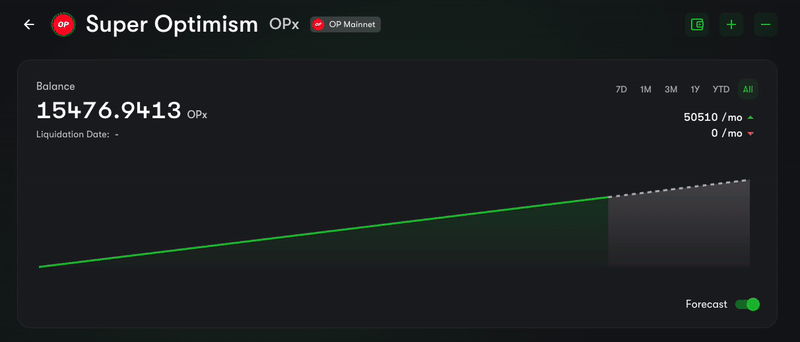
GIF of a "Flowing Balance" from the Superfluid Dashboard
We call this the FlowingBalance component and it's a great way to show the balance of a user in a dynamic and visually appealing way.
In this guide, we will show you how to make your balance dance. Let's get started!
Overview
The FlowingBalance component is designed to dynamically display a Super Token's balance that updates over time based on a specified flow rate, a starting balance and a starting date.
This guide breaks down the component into its core functionalities, including utility functions, custom hooks, and the component itself.
FlowingBalance leverages React's hooks to animate balance changes over time, simulating a continuous flow of currency.
It's particularly useful in applications that need to show real-time updates to a user's balance of Super Tokens, providing a visually appealing and responsive user interface.
Click here to show FlowingBalance Component code
import React, { useEffect, useState, useMemo, memo } from 'react';
import { formatEther } from 'viem';
// Constants
export const ANIMATION_MINIMUM_STEP_TIME = 40;
// Utility functions
export const absoluteValue = (n: bigint) => {
return n >= BigInt(0) ? n : -n;
};
export function toFixedUsingString(numStr: string, decimalPlaces: number): string {
const [wholePart, decimalPart] = numStr.split('.');
if (!decimalPart || decimalPart.length <= decimalPlaces) {
return numStr.padEnd(wholePart.length + 1 + decimalPlaces, '0');
}
const decimalPartBigInt = BigInt(`${decimalPart.slice(0, decimalPlaces)}${decimalPart[decimalPlaces] >= '5' ? '1' : '0'}`);
return `${wholePart}.${decimalPartBigInt.toString().padStart(decimalPlaces, '0')}`;
}
// Hooks
export const useSignificantFlowingDecimal = (
flowRate: bigint,
animationStepTimeInMs: number,
): number | undefined => useMemo(() => {
if (flowRate === BigInt(0)) {
return undefined;
}
const ticksPerSecond = 1000 / animationStepTimeInMs;
const flowRatePerTick = flowRate / BigInt(ticksPerSecond);
const [beforeEtherDecimal, afterEtherDecimal] = formatEther(flowRatePerTick).split('.');
const isFlowingInWholeNumbers = absoluteValue(BigInt(beforeEtherDecimal)) > BigInt(0);
if (isFlowingInWholeNumbers) {
return 0; // Flowing in whole numbers per tick.
}
const numberAfterDecimalWithoutLeadingZeroes = BigInt(afterEtherDecimal);
const lengthToFirstSignificantDecimal = afterEtherDecimal
.toString()
.replace(numberAfterDecimalWithoutLeadingZeroes.toString(), '').length; // We're basically counting the zeroes.
return Math.min(lengthToFirstSignificantDecimal + 2, 18); // Don't go over 18.
}, [flowRate, animationStepTimeInMs]);
const useFlowingBalance = (
startingBalance: bigint,
startingBalanceDate: Date,
flowRate: bigint
) => {
const [flowingBalance, setFlowingBalance] = useState(startingBalance);
const startingBalanceTime = startingBalanceDate.getTime();
useEffect(() => {
if (flowRate === BigInt(0)) return;
let lastAnimationTimestamp = 0;
const animationStep = (currentAnimationTimestamp: number) => {
const animationFrameId = window.requestAnimationFrame(animationStep);
if (
currentAnimationTimestamp - lastAnimationTimestamp >
ANIMATION_MINIMUM_STEP_TIME
) {
const elapsedTimeInMilliseconds = BigInt(
Date.now() - startingBalanceTime
);
const flowingBalance_ =
startingBalance + (flowRate * elapsedTimeInMilliseconds) / BigInt(1000);
setFlowingBalance(flowingBalance_);
lastAnimationTimestamp = currentAnimationTimestamp;
}
return () => window.cancelAnimationFrame(animationFrameId);
};
let animationFrameId = window.requestAnimationFrame(animationStep);
return () => window.cancelAnimationFrame(animationFrameId);
}, [startingBalance, startingBalanceTime, flowRate]);
return flowingBalance;
};
// FlowingBalance Component
const FlowingBalance: React.FC<{
startingBalance: bigint;
startingBalanceDate: Date;
flowRate: bigint;
}> = memo(({ startingBalance, startingBalanceDate, flowRate }) => {
const flowingBalance = useFlowingBalance(
startingBalance,
startingBalanceDate,
flowRate
);
const decimalPlaces = useSignificantFlowingDecimal(
flowRate,
ANIMATION_MINIMUM_STEP_TIME
);
return (
<div className="flowing-balance">
{decimalPlaces !== undefined
? toFixedUsingString(formatEther(flowingBalance), decimalPlaces)
: formatEther(flowingBalance)}
</div>
);
});
export default FlowingBalance;
The component explicited in the code above is composed of the following parts:
- Constants: This section defines the minimum time interval between animation updates.
- Utility Functions: These functions are used to calculate the absolute value of a number and format a number to a specified number of decimal places.
- Hooks: These custom hooks are used to calculate the number of significant decimal places to display and update the flowing balance over time.
- FlowingBalance Component: This functional component uses the hooks and utility functions to render the flowing balance, taking
startingBalance,startingBalanceDate, andflowRateas props.
Constants
export const ANIMATION_MINIMUM_STEP_TIME = 40;
This constant defines the minimum time interval (in milliseconds) between animation updates. It's used to throttle the animation and ensure that updates occur no more frequently than every 40 milliseconds.
Utility Functions
absoluteValue
export const absoluteValue = (n: bigint) => {
return n >= BigInt(0) ? n : -n;
};
Converts a bigint to its absolute value. This function is crucial for calculations that require the non-negative form of a number.
toFixedUsingString
export function toFixedUsingString(numStr: string, decimalPlaces: number): string {
// Implementation details
}
Formats a number (expressed as a string) to a specified number of decimal places. This function is essential for displaying the balance in a user-friendly format, ensuring that the balance is rounded and displayed with a consistent number of decimal places.
Hooks
useSignificantFlowingDecimal
export const useSignificantFlowingDecimal = (flowRate: bigint, animationStepTimeInMs: number): number | undefined => {
// Hook logic
};
Determines the number of significant decimal places to display based on the flow rate and animation step time. This custom hook helps adjust the precision of the balance display dynamically, based on how quickly the balance is changing.
useFlowingBalance
const useFlowingBalance = (startingBalance: bigint, startingBalanceDate: Date, flowRate: bigint) => {
// Hook logic
};
Calculates and updates the flowing balance over time. This hook is the core of the component, using the requestAnimationFrame API to smoothly update the balance display at a rate that's throttled by ANIMATION_MINIMUM_STEP_TIME.
FlowingBalance Component
const FlowingBalance: React.FC<{startingBalance: bigint; startingBalanceDate: Date; flowRate: bigint;}> = memo(({ startingBalance, startingBalanceDate, flowRate }) => {
// Component logic
});
This functional component uses the above hooks and utility functions to render the flowing balance. It takes startingBalance, startingBalanceDate, and flowRate as props, calculating the current balance based on these inputs and displaying it in a formatted manner.
Usage Example
Below is an example of how to use the FlowingBalance component within your application.
<FlowingBalance startingBalance={BigInt("1000000000000000000")} startingBalanceDate={new Date('2024-01-01T00:00:00.000Z')} flowRate={BigInt("1000000000000000")} />
This component exemplifies how to combine React's capabilities with the performance of the Web APIs to create dynamic and responsive UIs. By breaking down the component into its constituent parts, developers can gain insights into its functionality and customize it according to their needs.
Sometimes, especially if you center your component using justifyContent: "center", the component may have a jumpy behaviour like below:
❌ 10000000
If you run into this issue, you can try to set a fixed width to the component like such:
<div style={{ display: "flex", fontSize: "1.2rem", fontWeight: "bold", justifyContent: "center" }}>
<div style={{ width: "135px", margin: "auto" }}>
<FlowingBalance startingBalance={BigInt("1000000000000000000")} startingBalanceDate={new Date('2024-01-01T00:00:00.000Z')} flowRate={BigInt("1000000000000000")} />
</div>
</div>
This should fix the jumpy behaviour and make the component flow smoothly like the example below:
✅ 10000000
Best practices
- Throttle the animation: Ensure that the animation updates occur at a reasonable interval, such as every 40 milliseconds. This helps prevent excessive CPU usage and ensures a smooth user experience.
- Use fixed width: If the component is jumpy, consider setting a fixed width to the component to ensure a smooth flow of the balance.
- Time conversion: When showing the flow rate and converting the blockchain value to a human-readable value (eg. wei/s to ETH/month),
ensure that the time conversion is accurate and consistent with the rest of Superfluid's time-based calculations:
- 1 year = 365 days
- 1 month = 1 year/12
- 1 day = 24 hours
- 1 hour = 60 minutes
- 1 minute = 60 seconds
- 1 second = 1000 milliseconds
- Current timestamp: Following Superfluid's implementation, it is recommended to use
Date.now()to get the current timestamp in milliseconds instead of using(await ethers.provider.getBlock('latest')).timestampfor example.